AI is transforming how e-commerce businesses predict and prepare for seasonal demand. By analyzing diverse data - like sales history, weather patterns, and social media trends - AI provides precise forecasts that help businesses avoid overstocking or running out of stock. Here’s what you need to know:
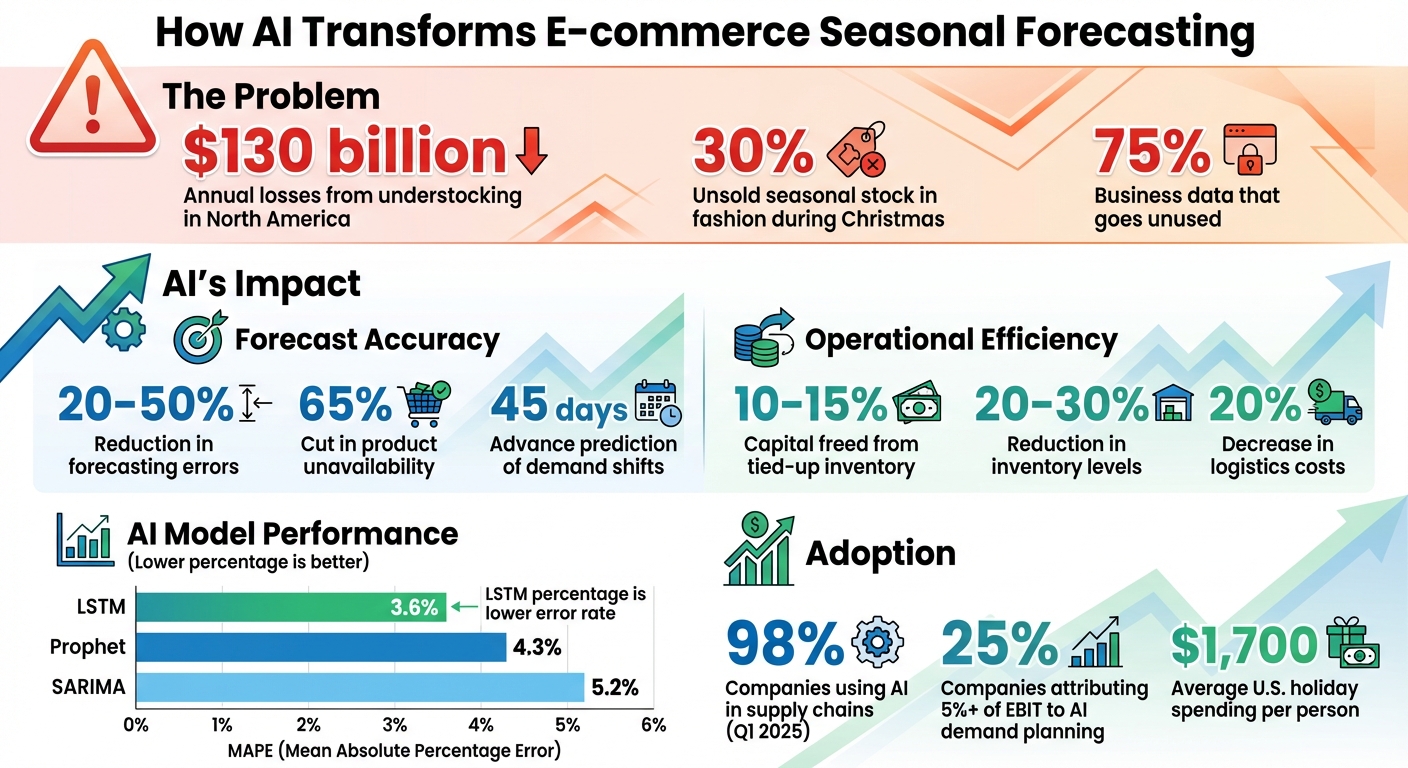
- Why it matters: Seasonal misjudgments can cost retailers billions. AI reduces forecasting errors by 20–50% and cuts product unavailability by 65%.
- How it works: AI uses internal data (e.g., sales history, promotions) and external signals (e.g., weather, search trends) to predict demand shifts up to 45 days ahead.
- Key benefits: Better inventory planning, fewer stockouts, and reduced excess stock, freeing up 10–15% of tied-up capital.
AI-powered tools like Forthcast simplify forecasting by automating data analysis, tagging promotions, and even handling new product launches. This ensures businesses stay ahead of demand fluctuations with minimal manual effort.
AI Forecasting Impact on E-commerce: Key Statistics and Benefits
How AI Identifies Seasonal Trends in E-commerce
What Are Seasonal Trends in E-commerce?
Seasonal trends in e-commerce are recurring patterns in consumer demand. These can range from shopping holidays and weather-related spikes to cultural events and even monthly pay cycles. They vary significantly by industry and region. For example, the fashion sector often deals with 30% unsold seasonal stock during Christmas, while understocking in North America has led to losses estimated at $130 billion. To avoid issues like overstocking or missed sales opportunities, understanding the timing, duration, and specific products impacted by seasonal demand is crucial. AI steps in here by combining a mix of internal and external data sources to forecast these trends with precision.
Data Sources AI Uses for Seasonal Forecasting
To create accurate forecasts, AI pulls data from numerous streams, painting a detailed picture of seasonal demand.
Internal sales data is the starting point. This includes SKU-level sales history, product attributes (like color, size, and brand), and inventory-related factors such as stockouts and lead times. Marketing signals also play a pivotal role. AI examines promotional calendars, ad spend, discount history, and price changes to distinguish between organic demand spikes and those driven by marketing efforts.
External data adds another layer of depth. For instance, AI analyzes weather patterns, Google Search trends, and social media sentiment to anticipate short-term demand shifts before they appear in sales figures. Broader economic and supply chain indicators also come into play. The Baltic Dry Index, which hit 2,008 points in August 2025, can reveal shipping delays, while rising copper prices - reaching $10,028 per tonne in 2025 - can influence demand for electronics and hardware. AI also tracks cultural and temporal patterns, such as regional holidays and pay cycles, to identify trends that traditional forecasting methods might overlook.
| Data Category | Signals AI Analyzes |
|---|---|
| Internal | SKU sales history, stockouts, return rates, product attributes (color, size, fabric) |
| Marketing | Ad spend (ROAS), promotional calendars, discount history, price changes |
| External | Weather patterns, Google Search trends, social media sentiment |
| Macro | Baltic Dry Index, commodity prices, tariff changes |
| Temporal | Paydays, holidays (Ramadan, Diwali), seasonal temperature shifts |
By integrating these diverse data points, AI models provide a more nuanced and accurate understanding of seasonal demand.
Why AI Outperforms Traditional Forecasting Methods
Traditional forecasting often relies on static assumptions, which can fall short during unpredictable periods. AI, on the other hand, adapts in real-time, significantly reducing prediction errors.
The standout feature of AI is its ability to learn and adjust continuously. As fresh data becomes available, AI retrains itself, allowing it to spot trends early - whether it’s a product going viral on TikTok or a sudden cold snap increasing the demand for heaters. AI can predict these shifts up to 45 days in advance, enabling businesses to adjust inventory proactively. Unlike traditional methods, which might misinterpret stockouts as low demand, AI estimates lost sales, offering a clearer picture of potential demand.
Another advantage is the level of detail AI provides. Instead of broad, category-level forecasts, AI delivers SKU-specific predictions across multiple sales channels and time frames - whether it’s 30, 60, or 90 days. For new products without historical sales data, AI uses attribute-based forecasting, analyzing elements like color, fabric, and price. It can even process images to identify patterns from similar products. As of Q1 2025, 98% of companies have incorporated AI into their supply chains, with 25% attributing over 5% of their EBIT to AI-powered demand planning.
"Using only past sales to predict future demand is like driving while looking in the rearview mirror. You can see where you've been, but it tells you nothing about what's ahead." - InventoryInsight
Forthcast leverages these advanced AI capabilities to analyze a wide range of data and improve inventory planning, ensuring e-commerce businesses stay ahead of seasonal demand changes.
AI Demand Forecasting at ASOS: Building a Scalable Machine Learning System to Forecast for Thousands
Preparing Your E-commerce Data for AI Forecasting
Getting your data in shape is the first step toward accurate AI forecasting. AI thrives on high-quality, well-structured data, and without it, seasonal predictions can fall flat. Here’s a surprising fact: about 75% of business data goes unused - a goldmine of untapped potential. The challenge? Turning raw sales records into clean, structured datasets that AI can actually learn from.
Cleaning and Structuring Historical Data
To start, focus on collecting your historical sales data at the SKU level rather than broader categories. AI works best with detailed information, which helps it pinpoint when specific products experience seasonal demand spikes. Make sure all your date formats are standardized to MM/DD/YYYY, and use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines to pull and clean data from platforms like Shopify, BigQuery, or your warehouse systems.
For unstructured data, fill in missing values using methods like the mean, median, or K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) to maintain the integrity of your patterns. Clean out anomalies such as fraudulent orders or data entry errors using techniques like Isolation Forest or Z-score analysis - these outliers can seriously mess with your seasonal trends.
To enrich your dataset, add features like time-based elements (day, month, holidays), product attributes (price, brand), and marketing data (discounts, ad spend). This additional context helps AI connect the dots between external drivers and seasonal demand. Don’t forget to label external events, so your model can account for unusual factors beyond regular sales trends.
Tagging Promotions and Stockouts
Historical events like promotions and stockouts can distort seasonal patterns if left untagged. For instance, a flash sale on 07/04/2025 might double your sales for a few days, but the AI needs to understand this spike was promotion-driven, not part of a typical seasonal cycle. Be sure to tag every promotional event - whether it’s an email campaign, social media push, or discount code - to help the model distinguish between organic demand and marketing-induced surges.
Stockouts are another critical factor. Traditional forecasting models often see zero sales as zero demand, but AI can use stockout-tagged data to estimate lost sales and predict true demand. Linking your marketing platforms - like Meta, Google, or TikTok Ads - provides additional context by correlating ad spend with shifts in sales velocity. Once these elements are addressed, you’ll be ready to tackle forecasting for new or seasonal SKUs.
Forecasting with Limited Data for New or Seasonal SKUs
New products often face a "cold start" problem since there’s no historical data to rely on. One way to overcome this is by using product analogs. AI can identify similar products based on attributes like category, brand, price, color, or design, and then apply their seasonal patterns to the new SKU. For example, if you’re introducing a new winter jacket, the AI can analyze how similar jackets performed in previous winters.
When data is sparse, grouping similar items into clusters can help build a stronger statistical foundation. For industries like fashion, multivariate forecasting can dive into patterns across size, color, and fit to predict demand at the SKU level.
You can also supplement your internal data with external signals. Monitoring early web traffic, social media buzz, and trending topics allows you to adjust demand predictions right after launch. For high-uncertainty products - like limited editions or collaborations - combining AI forecasts with human expertise ensures no context is overlooked.
Platforms like Forthcast excel in tackling these challenges, offering tools for early pattern detection, anomaly identification, and SKU-level analysis to navigate data scarcity effectively.
How AI Models Predict Seasonal Demand
AI models use clean, structured data to forecast future demand by blending traditional statistical methods like ARIMA and Prophet with advanced machine learning techniques. This combination helps capture steady trends while adapting to the unpredictable shifts that often challenge older forecasting methods.
Core Modeling Approaches
AI-driven forecasting employs a range of modeling techniques tailored to specific scenarios. For example, SARIMA is ideal for identifying consistent seasonal patterns in stable product categories, while Prophet shines when dealing with incomplete data or holidays that shift annually. For more intricate patterns, LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) neural networks excel at decoding sequential complexities. In performance tests, LSTM demonstrated a Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) of 3.6%, outperforming Prophet (4.3%) and SARIMA (5.2%).
Many modern AI systems also utilize multivariate forecasting, analyzing data across various dimensions like product lines, locations, and attributes such as size, color, or fit. This approach reveals correlations that might otherwise go unnoticed. For example, a spike in demand for one color variant could predict increased interest in similar styles. Advanced tools even incorporate knowledge graphs to map contextual relationships, such as how Diwali or Ramadan might drive demand for specific product categories in particular regions. These techniques enable AI to adapt dynamically to emerging seasonal patterns.
Detecting Recurring Patterns and Adaptive Learning
AI takes forecasting a step further by continuously refining its predictions through adaptive learning. It identifies seasonality by analyzing non-linear relationships across internal data (like sales and inventory) and external factors such as weather, social media trends, and macroeconomic indicators. By de-seasonalizing historical data, AI can separate true seasonal demand from one-off anomalies like promotional events. For instance, without this adjustment, a Black Friday sale could be misinterpreted as a recurring demand surge, skewing future forecasts.
"Seasonality isn't just about holidays - it's a multi-layered pattern influenced by regional events, economic shifts, and consumer behavior cycles." - AgentiveAIQ
AI systems retrain themselves as new data becomes available, enabling them to detect demand spikes more than 45 days in advance. This allows businesses to rebalance inventory proactively. By Q1 2025, 98% of companies reported integrating AI into their supply chains to harness these capabilities.
Forecast Horizons for Seasonal Planning
AI supports forecasts across short, medium, and long-term horizons, each serving a distinct purpose. Short-term forecasts guide immediate replenishment during sudden demand surges. Medium-term forecasts align with promotional campaigns and marketing strategies, while long-term forecasts are essential for pre-season manufacturing and managing extended lead times.
For example, Forthcast's platform provides 6-month SKU-level demand forecasts, enabling precise inventory planning. It tracks forecast accuracy by measuring both bias (direction of error) and accuracy (magnitude of error), ensuring you can rely on its predictions to fine-tune your strategy. By combining statistical pattern recognition with machine learning’s adaptability, Forthcast selects the most effective forecasting method for each SKU, ensuring reliable predictions across your entire catalog. These accurate forecasts empower businesses to make proactive inventory adjustments, delivering the operational benefits discussed earlier.
sbb-itb-499c055
Using Seasonal AI Forecasts to Optimize Inventory Decisions
Once you have dependable seasonal forecasts, the next step is turning those predictions into actionable inventory strategies. This involves determining how much to order, when to place orders, and how to adjust for events like promotions - all while avoiding excessive cash tied up in stock or the risk of running out.
Aligning Inventory with Predicted Demand
Use your AI-generated forecast to calculate order quantities by factoring in predicted demand, supplier lead times, and safety stock. For instance, if your forecast predicts sales of 500 units over the next 60 days and your supplier requires 30 days to deliver, you’ll need to order immediately to cover that demand. Don’t forget to include a safety stock buffer - often around 70% of your peak-season inventory - to handle unexpected surges.
AI-driven forecasting can cut the capital tied up in inventory by 10–15% while maintaining or even improving product availability. This is achieved by dynamically adjusting safety stock based on seasonal trends. During slower months, you can lower stock levels to free up cash, then increase buffer stock as peak seasons approach. Tools like Forthcast simplify this process by automating reorder decisions with 6-month SKU-level projections and alerts that consider your specific lead times. These forecasts also help you adjust for promotional events and market shifts.
Adjusting for Promotions and Events
Big U.S. shopping events such as Black Friday, Cyber Monday, or July 4th require special planning. AI models need to account for the extra demand generated by promotions, rather than treating these events as typical seasonal fluctuations. By feeding your AI system details like promotional calendars, planned ad spend, and email campaign schedules, it can more accurately predict demand spikes.
For example, in September 2024, a mid-sized skincare brand noticed an increase in search volume for hydrating serums, coupled with early cold weather alerts. The AI system triggered a supplier reorder and adjusted ad spend accordingly, leading to a 27% higher sell-through compared to the previous year - with zero stockouts. Once promotional adjustments are in place, the next step is managing the risks of overstock and stockouts.
Balancing Overstock and Stockout Risks
The key is finding the middle ground between overstocking - which ties up cash and raises storage costs - and understocking, which leads to missed sales opportunities. AI can help by prioritizing high-velocity and high-margin SKUs when budgets are tight, ensuring your resources are allocated where they’ll generate the best returns.
The stakes are high: understocking costs North American retailers an estimated $130 billion in lost sales annually, while in the fashion industry, about 30% of seasonal stock typically goes unsold during the Christmas period. To strike the right balance, track metrics like Days of Supply (DOS) and Stock-out Rate. AI tools can also monitor forecast accuracy, helping you identify any bias or gaps in predictions so you can fine-tune your risk tolerance over time.
"The AI doesn't replace your judgment - it amplifies it." - Ashley Lenz, Product Researcher, Coefficient
To maintain optimal inventory levels, combine reliable AI forecasts with strategic human insights. Let AI handle products with consistent demand, but for new or short-life products, expert input is invaluable. This is especially true when external factors - like port closures or sudden regulatory changes - disrupt the supply chain in ways the AI model may not yet reflect.
Improving and Monitoring Seasonal AI Forecasts
When it comes to AI forecasting, it’s not a one-and-done process. The best e-commerce businesses treat it as an ongoing cycle - constantly comparing predictions to actual sales, fine-tuning models, and adapting to shifting market conditions. This iterative approach can cut forecast errors by anywhere from 20% to 50% compared to static methods. To make the most of your forecasting, you’ll need to measure performance regularly and identify areas for improvement.
Tracking Forecast Accuracy
To gauge how well your forecasts are performing, focus on SKU-level accuracy over 30-, 60-, and 90-day periods. Two key metrics to track are MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error) and Forecast Bias. MAPE gives you a clear picture of overall accuracy, while Forecast Bias helps you spot consistent over- or under-predictions - both of which can directly affect how much safety stock you need.
Set a routine for reviewing forecasts - weekly or monthly - and compare AI predictions to real sales data. This process will help pinpoint which product categories, sales channels, or seasonal windows need adjustments. Tools like Forthcast can simplify this by automating accuracy tracking, analyzing both bias and magnitude, and helping you make smarter risk adjustments.
Adapting Forecasts for Changing Trends
Once you’ve got a handle on your forecast accuracy, the next step is keeping your models in sync with shifting market trends. Seasonal patterns don’t stay static, and neither should your AI. Feed your model real-time external signals like weather data, social media trends from platforms like TikTok and Instagram, macroeconomic indicators (e.g., the Consumer Price Index), and shipping metrics like the Baltic Dry Index. These signals can detect demand shifts up to 45 days in advance, giving you a crucial window to adjust inventory before sales trends materialize.
Don’t forget to update external driver calendars to account for changes like tariffs that can influence costs and consumer behavior. If you’re dealing with products that have regional variations - like summer gear selling in different seasons depending on the hemisphere - make sure your model accounts for those differences. A human-in-the-loop approach works well here: let AI handle products with consistent demand and a solid sales history, but rely on expert input for newer items, short-lifecycle products, or unexpected disruptions like port closures.
Building Feedback Loops
To take your forecasting to the next level, establish a closed feedback loop that refines your model with every cycle. After each forecast, compare predictions to actual outcomes and feed that data back into the system. The more data your AI model processes, the better it gets at self-optimizing.
"AI models can 'self-optimise' and improve over time as they are exposed to more data and feedback, resulting in increasingly accurate forecasts." - Slimstock
Keep your historical data clean by removing one-off anomalies. It’s also a good idea to measure Forecast Value-Added (FVA) to see if manual overrides or external data sources are actually improving your accuracy. Set up automated alerts for significant deviations between forecasted and actual demand, so your team can react quickly and recalibrate in real time. Combining automated learning with strategic human oversight is what separates good forecasting from exceptional forecasting.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing seasonal forecasting, shifting it from a reactive, spreadsheet-driven task to a forward-thinking, predictive process. By combining historical data with real-time factors like weather patterns, social trends, and economic indicators, AI can cut forecast errors by as much as 25%. For U.S. retailers, where holiday spending averages $1,700 per person, this level of precision can mean fewer stockouts and a direct boost to revenue.
But it’s not just about accuracy. AI-powered platforms also deliver operational efficiencies, reducing inventory levels by 20–30% and logistics costs by 20%. These savings free up working capital and further highlight AI’s edge over traditional methods. Tools like Forthcast take it a step further by automating the entire forecasting process. From triggering smart reorder alerts to identifying sales anomalies and projecting SKU-level demand up to six months ahead, these platforms allow teams to focus on strategic growth instead of wrestling with data.
What’s more, platforms like Forthcast handle the complexities of seasonal demand without requiring a dedicated data science team. They automatically adjust for promotions, manage bundle relationships, and even forecast new SKU launches by substituting product data. With features like bias tracking, accuracy measurement, and customizable forecast enhancements, businesses gain a clear view of prediction performance and actionable insights for improvement. These capabilities not only streamline operations but also lay the groundwork for a more resilient and adaptive business strategy.
FAQs
How does AI use data like weather and social media to predict seasonal e-commerce trends?
AI taps into real-time external data, like weather forecasts and social media trends, to sharpen predictions for seasonal e-commerce demand. For instance, temperature shifts or rainfall patterns can signal a rise in demand for items like jackets, swimwear, or heaters. At the same time, social media trends - think viral hashtags or influencer shoutouts - highlight emerging consumer interests, turning fleeting moments into actionable insights.
When you mix these external cues with historical sales data, promotional schedules, and inventory stats, AI delivers more accurate and dynamic forecasts. Tools like Forthcast take it a step further by providing SKU-level predictions, helping businesses stock up on the right products at the right time - avoiding the headaches of excess inventory or empty shelves.
How does AI improve seasonal demand forecasting compared to traditional methods?
AI is transforming how businesses handle seasonal demand forecasting, cutting errors by as much as 25% and spotting demand surges as early as 45 days ahead. By analyzing real-time and external data nonstop, it reveals patterns that older forecasting methods often overlook.
On top of that, AI streamlines inventory management, boosting seasonal sell-through rates by up to 32%. It prevents stockouts, reduces surplus inventory, and helps businesses make smarter, faster decisions. The result? A more efficient and profitable way to tackle seasonal demand challenges.
How can businesses prepare their data for AI-driven seasonal forecasting?
To get accurate results from AI forecasting, businesses need to start with clean, complete, and well-organized data. Begin by gathering relevant historical data like sales records, SKU details, inventory levels, pricing, and promotional activities. Including external factors - such as holiday calendars, weather patterns, or real-time search trends - can further improve the model’s precision.
Next, focus on cleaning your data. Remove duplicates, fix errors, and address any gaps. Standardizing formats is key - for instance, use MM/DD/YYYY for dates and ensure monetary values are recorded in dollars with two decimal places. Organize your data at a practical level, such as daily or weekly summaries, and split it into training and validation sets. This allows the AI to identify patterns effectively.
By following these steps, businesses can leverage AI tools to make accurate seasonal demand forecasts and improve inventory management decisions.