Managing inventory effectively relies on two critical factors: accuracy and bias in demand forecasts. Accuracy ensures predictions align closely with actual sales, while bias reveals if forecasts consistently overestimate or underestimate demand. Ignoring these can lead to overstocking or stockouts, driving up costs and lost revenue.
AI-driven forecasting can cut lost sales by up to 65% and reduce inventory levels by 20–30%, but many AI models operate as "black boxes", offering little insight into their predictions. Explainable AI (XAI) solves this by breaking forecasts into clear components like seasonality, trends, and promotions, helping businesses identify and correct errors. For example, an agribusiness improved forecast accuracy by 8%, reduced scheduling time by 96%, and added $30 million in gross margins using XAI.
Key takeaways:
- Bias: Consistent over/underestimation of demand leads to stockouts or excess inventory.
- Accuracy: Measures how close predictions are to actual sales, using metrics like MAPE and WMAPE.
- Explainable AI: Provides transparency into predictions, enabling better decisions and trust.
Revolutionizing Demand Forecasting and its Enterprise Impact using Causal AI and Agents
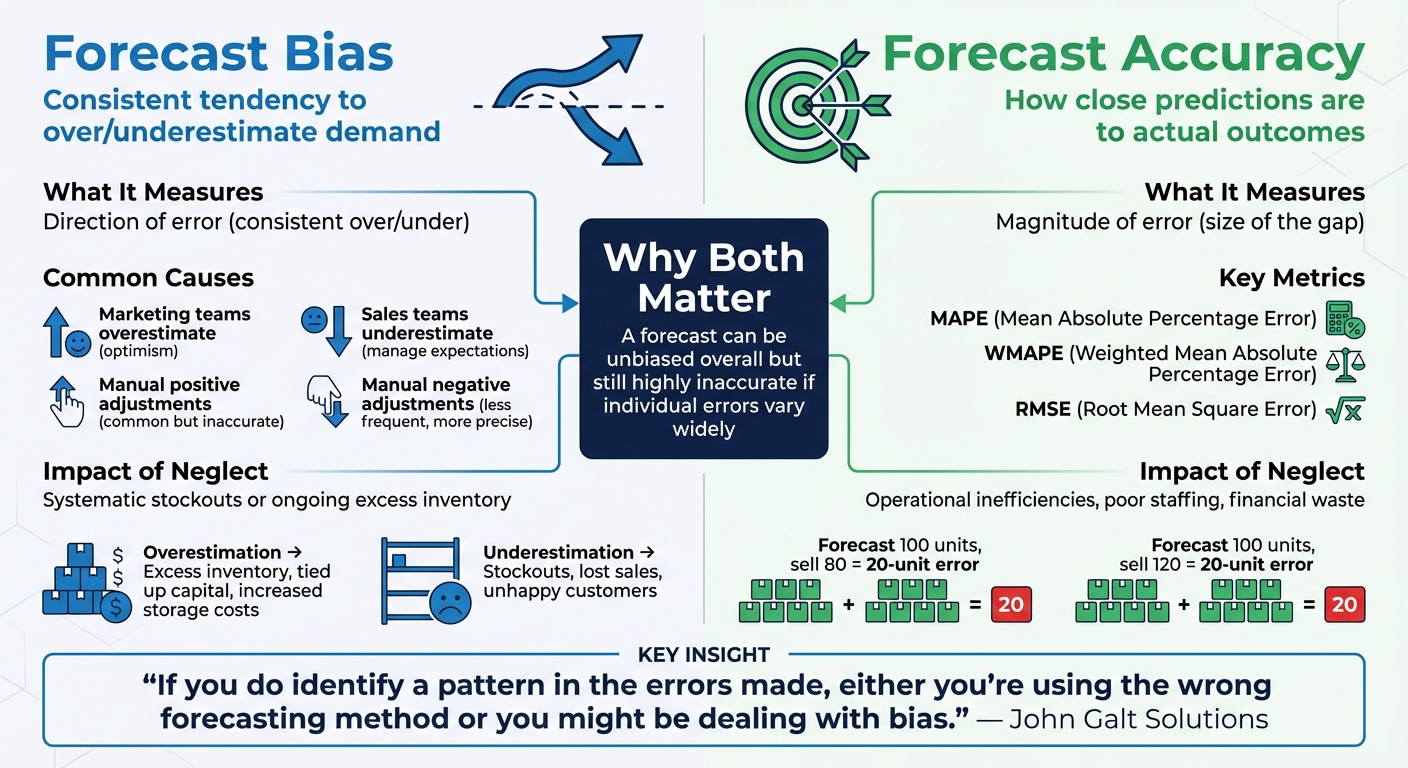
Understanding Bias and Accuracy in Forecasting
Forecast Bias vs Accuracy: Impact on Inventory Management
What is Forecast Bias?
Forecast bias refers to a consistent tendency to either overestimate or underestimate demand. Unlike random errors, bias exhibits a recurring pattern that skews your predictions in one direction.
Bias often sneaks in through departmental habits. For example, marketing teams may overestimate demand for a new product due to optimism, while sales teams might underestimate to manage expectations. Human intervention also plays a role. A study of 30 million forecasts at the SKU-store-day level revealed that manual positive adjustments are more common but often inaccurate, whereas negative adjustments, though less frequent, tend to be more precise.
The consequences of bias are costly. Overestimations lead to excess inventory, which ties up capital and increases storage expenses. Underestimations, on the other hand, cause stockouts, leading to lost sales and unhappy customers.
What is Forecast Accuracy?
Forecast accuracy measures how close your predictions are to actual outcomes. For instance, if you forecast sales of 100 units but only sell 80, the error is 20 units. Similarly, forecasting 100 but selling 120 results in the same 20-unit error.
Several metrics help evaluate forecast accuracy:
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE)
- Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error (WMAPE)
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
WMAPE is particularly valuable in inventory management because it weighs errors based on sales volume or value. For example, a 10% error on a high-demand product impacts operations more than the same error on a slow-moving item.
"Accurate sales forecasts help make operations more efficient, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction."
- Miguel Arantes et al., Electronic Research Archive
Poor accuracy disrupts everything from staffing and promotions to cash flow management. A study published in April 2025 by Miguel Arantes and colleagues analyzed data from 1,115 Rossmann stores. Using a hybrid model called "LR_XGBoost", they achieved a test WMAPE of 10.18%. This approach combined advanced AI techniques with interpretability, offering both high accuracy and clear insights into how factors like holidays and promotions influence sales.
Understanding both bias and accuracy is key to making informed decisions that reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Why Both Metrics Matter
Bias and accuracy are distinct yet interconnected. Bias reflects the direction of error - whether forecasts consistently overshoot or undershoot demand - while accuracy measures the size of the error. A forecast can be unbiased overall (with errors balancing out over time) but still highly inaccurate if individual errors vary widely.
Focusing only on accuracy without addressing bias can lead to recurring patterns of error. For example, you might hit the overall forecast number but consistently miss in specific categories or seasons. Ignoring accuracy, however, makes forecasts unreliable for daily operations, leading to inefficiencies and financial losses.
"If you do identify a pattern in the errors made, either you're using the wrong forecasting method or you might be dealing with bias."
| Metric | What It Measures | Impact of Neglect |
|---|---|---|
| Bias | Directional error (consistent over/under) | Systematic stockouts or ongoing excess inventory |
| Accuracy | Magnitude of error (size of the gap) | Operational inefficiencies, poor staffing, financial waste |
The Challenges of Traditional Forecasting Methods
Traditional forecasting methods often fall short, introducing errors that undermine bias control and accuracy. These methods rely heavily on historical data, which acts as a lagging indicator - providing insights into past performance but failing to predict future trends effectively. This reactive approach keeps businesses stuck in a cycle of responding to changes rather than preparing for them.
"Most forecasting today is fundamentally backward-looking. It relies on historical data, and this creates a blind spot where we're focusing on a lagging indicator. It tells us what happened yesterday and not necessarily what's coming tomorrow."
- Matt Morton, Senior Director of Engineering, GAINS
Complicating matters further, traditional methods struggle with complex relationships - like the impact of promotions or local market conditions. These systems are also ill-equipped to handle "change points", such as significant shifts in customer behavior triggered by events like COVID-19. Instead, they continue to rely on outdated patterns, which leads to recurring biases that are difficult to correct.
Common Causes of Forecasting Bias
Manual adjustments are a major source of error. When planners don't trust their forecasting tools, they often override predictions based on instinct rather than data. This manual intervention compounds inaccuracies, especially when legacy systems fail to identify the root causes of bias or offer solutions to address them.
Outdated historical data is another culprit. Legacy systems tend to overemphasize older data, ignoring current market dynamics. For instance, a product that performed well two years ago might now face entirely different demand drivers, yet these outdated systems continue to give undue weight to past trends.
Resolving these issues is essential for integrating more advanced tools, like explainable AI, into forecasting processes.
Accuracy Problems in Legacy Systems
Beyond bias, traditional systems face significant accuracy challenges that hinder their effectiveness.
One common issue is the misalignment of accuracy metrics. Legacy systems often evaluate accuracy over a 30-day period, which may not align with actual lead times. This mismatch can result in stockouts or overstock situations, even when forecasts appear accurate on paper.
These systems also fail to account for complex variables. Factors like weather, raw material costs, economic trends, and real-time customer behavior play a critical role in shaping demand. For example, a study involving 1,115 Rossmann stores found that promotions and holidays were key drivers of accurate forecasts. However, simple regression models lack the flexibility to incorporate such nuanced factors.
New product launches present another major challenge. Traditional methods rely on extensive historical data to generate reliable forecasts. This means businesses are often left guessing or waiting months to gather enough sales history when introducing new products or working with unfamiliar suppliers. Without the ability to substitute data from similar products, companies face costly delays or inaccuracies.
The trade-off is clear: simpler models may offer transparency but often deliver poor results, while more complex models improve accuracy but become "black boxes" that are hard for stakeholders to trust. By moving away from these outdated methods to AI-driven forecasting, businesses can achieve a 20–30% reduction in forecast error. However, success hinges on addressing both bias and accuracy simultaneously.
sbb-itb-499c055
How Explainable AI Improves Demand Forecasting
Explainable AI (XAI) is changing the game for demand forecasting by tackling two critical challenges: forecast bias and accuracy. Unlike traditional "black box" models that leave planners in the dark, XAI brings both precision and clarity. It not only delivers accurate forecasts but also explains the reasoning behind them, highlighting the factors that drive each prediction.
Transparent Decision-Making with Explainable AI
One of the biggest hurdles in trusting AI forecasts is the lack of clarity about why a system makes specific predictions. XAI addresses this by using tools like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations), which break down how much each variable - such as promotions, weather, or seasonal trends - contributes to a forecast. This level of detail helps planners distinguish between legitimate data-driven forecasts and errors that might need adjustment.
"Black box algorithms often show strong performance. But because we cannot see how they arrive at predictions, they are difficult to trust." - Yvonne Badulescu, AI Researcher
By decomposing forecasts, XAI clarifies whether demand spikes are caused by market changes or random fluctuations. This transparency encourages stakeholders to trust and act on forecasts, reducing the need for manual overrides that often introduce new biases. With this foundation, businesses can adopt advanced techniques to sharpen forecast accuracy even further.
Advanced Forecasting Techniques
Modern AI systems excel at analyzing a mix of internal and external variables, uncovering complex patterns that older methods often miss. Before generating forecasts, XAI can detect anomalies and apply change point detection to identify major behavioral shifts, like those caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. This ensures that models focus on relevant, up-to-date data rather than outdated trends.
For example, a study involving 1,115 Rossmann stores showcased the effectiveness of hybrid models. By combining XGBoost for accuracy with Linear Regression for interpretability, the model achieved a test weighted mean absolute percentage error of just 10.18%. This approach balanced the predictive power of machine learning with the transparency needed for decision-makers to trust and act on the insights.
Real-world applications highlight the benefits. Danone leveraged machine learning to reduce forecast errors by 20% and cut lost sales by 30%. Meanwhile, a global biopharma company improved customer retention by 11% through AI-driven inventory management that ensured product availability. These successes stem from AI's ability to adapt in real-time, recalibrating predictions to reflect emerging trends before they disrupt inventory levels.
Data-Driven Insights for Better Inventory Decisions
At the SKU level, explainable AI provides a granular view of inventory needs, uncovering details that aggregated forecasts often miss. By analyzing each product individually - factoring in its lifecycle, seasonality, and demand drivers - AI creates tailored reorder points and safety stock levels, helping businesses avoid both overstocking and stockouts.
Platforms like Forthcast take this a step further by combining statistical methods with machine learning to select the best forecasting approach for each SKU. These systems track both bias (the direction of error) and accuracy (the size of the error), giving businesses a clear understanding of forecast performance. Features like anomaly detection, SKU-level breakdowns, and the ability to substitute data from mature products for new launches enable merchants to make informed inventory decisions based on reliable predictions.
The financial benefits are hard to ignore. AI-driven forecasting can lower inventory carrying costs by 20% to 35% and reduce stockouts and overstocks by as much as 85%. During the Thanksgiving to Cyber Monday period in November 2024, Walmart used AI-powered models to anticipate regional demand surges, serving 200 million customers by dynamically adjusting inventory across its network. This kind of precision - combining clarity with accuracy - sets modern explainable AI apart from outdated systems, enabling businesses to achieve smarter inventory management and better outcomes overall.
Practical Steps for Implementing Explainable AI
Preparing Your Data for AI Integration
The first step is making sure your data is clean and well-organized. Missing values? Address them with methods like probabilistic imputation or median substitution. Outliers? Flag them to figure out if they’re errors or legitimate events, like unexpected spikes from promotions. Adding anomaly detection to your data prep process can help filter out errors while validating unusual but valid occurrences.
Another useful technique is change point detection, which highlights shifts in customer behavior. This ensures your model focuses on current patterns instead of outdated trends. For time series data, break it into its main components: trend (long-term direction), seasonality (repeating cycles), and recency (recent observations). This breakdown helps you understand what’s driving your forecasts and where you might need to make adjustments.
To avoid overemphasizing similar inputs, standardize features (usually to a 0–1 range) and remove variables with correlations higher than 0.80. And for rare but critical events - like product backorders - use synthetic oversampling techniques like ADASYN or SMOTE to ensure your model learns from these essential scenarios. Once your dataset is ready, the next step is keeping an eye on performance.
Monitoring and Measuring Forecast Performance
Once your data is prepped, it’s time to monitor how well your forecasts perform. This means going beyond simply checking if predictions match sales. Modern systems break forecasts into components like trend, seasonality, recency, and noise. This allows you to pinpoint whether errors come from outdated historical patterns or overreacting to recent changes. Automated anomaly detection can flag unusual predictions and prompt human review when the AI spots something that doesn’t fit established trends.
Pay attention to specific error metrics to gauge performance. Metrics like Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error (WMAPE) provide a detailed view of how your model performs across products with different sales volumes. For instance, a 2025 study analyzing data from 1,115 Rossmann stores showed a hybrid model (XGBoost plus Linear Regression) achieving a WMAPE of 10.18%, offering both predictive accuracy and the transparency retail managers wanted. Another helpful metric is Theil's U statistic, which compares your AI’s accuracy against basic forecasting methods. A value below 1.0 means your AI is outperforming simpler approaches.
Tools like Forthcast make this process easier with features like a self-assessing accuracy engine that tracks bias (direction of error) and accuracy (size of error). This dual-metric approach, combined with anomaly detection and SKU-level breakdowns, gives businesses a clear view of forecast reliability - all for as little as $19.99 per month. Use global explanation tools like SHAP to understand your model’s overall priorities, and local tools like LIME to audit individual predictions. These insights help validate your model’s performance and ensure it aligns with your business needs.
Customizing AI Forecasting for Your Business
With solid data prep and performance tracking in place, it’s time to tailor your AI forecasting to suit your specific challenges. Start by adding external variables (like weather, holidays, promotions, or economic data) to account for factors beyond historical sales. Choose the right granularity level for your forecasts - whether it’s SKU, store, or region - to make inventory decisions more precise.
Adjust forecasts to match your risk tolerance with service level customization. For example, if stockouts are more costly than excess inventory for certain products, configure the system to prioritize higher safety stock levels. Enable "what-if" simulations to test scenarios like introducing a new product or adjusting prices by 10%, so you can make informed decisions before committing resources. Walmart, for example, uses tailored AI models during the Thanksgiving to Cyber Monday period to manage demand surges for 200 million customers, dynamically adjusting inventory across stores and online channels.
Consider hybrid modeling approaches that strike a balance between accuracy and transparency. One agribusiness company unified 72 million rows of data from 18 sources (like shipping documents and manufacturing specs) to shift from weekly to daily demand forecasting. This change reduced production scheduling time by 96%, improved on-time deliveries by 2%, and added about $30 million in gross margin gains. For rare events like backorders, synthetic oversampling ensures the AI learns from these scenarios. Forthcast also offers tailored enrichments for promotions and trend detection, helping businesses fine-tune their forecasts while maintaining the transparency needed to trust AI-driven recommendations.
Conclusion
Explainable AI strikes a balance between accuracy and trust. While traditional "black box" models might deliver precise predictions, their lack of transparency often leads planners to override decisions - usually with negative consequences. Explainable AI, on the other hand, shines a light on the key factors driving predictions, empowering businesses to make confident, informed adjustments.
"True explainable AI doesn't just provide accurate predictions – it offers insights that drive informed decision-making and trust"
This transparency doesn't just enhance trust - it directly impacts the bottom line. AI-driven forecasting can deliver real financial benefits: reducing lost sales by up to 65%, cutting inventory levels by 20–30%, lowering dead stock write-offs from 8–12% to 2–4%, and improving inventory turnover ratios from 3.2 to 5.8. By combining clarity with strong predictive models, businesses build confidence and achieve better performance.
Platforms like Forthcast bring these principles to life with tools designed for everyday use. For $19.99 per month, it offers SKU-level forecasts up to six months in advance, anomaly detection, and a self-assessing accuracy engine that tracks both bias and accuracy. Its hybrid approach - merging statistical analysis with machine learning - adapts to your unique business while maintaining transparency. Customizable features like promotion forecasts and service level adjustments let you tailor the system to your specific needs and risk tolerance.
When forecasts clearly show their underlying drivers - be it seasonal trends, promotional impacts, or shifts in customer behavior - decision-makers can set smarter safety stock levels, reorder points, and purchasing strategies. This clarity reduces reliance on manual overrides, which research shows often worsen forecast accuracy. Instead of second-guessing the system, planners can focus on strategic decisions that propel the business forward.
Explainable AI lays the foundation for a responsive supply chain. Whether you're managing product bundles, launching new items, or navigating seasonal changes, transparent forecasting builds the confidence to act decisively. The payoff? Fewer stockouts, reduced excess inventory, and a leaner operation that satisfies customers while protecting profit margins. Balancing bias and accuracy through explainable AI is the key to smarter, more profitable inventory management.
FAQs
How does Explainable AI build trust in demand forecasting?
Explainable AI (XAI) transforms how businesses approach demand forecasting by shedding light on the inner workings of complex models. Unlike traditional "black box" AI systems, which often leave users guessing, XAI provides clear insights into the factors influencing predictions. Whether it's seasonality, promotions, or market trends, XAI breaks down these elements, showing exactly how forecasts are shaped. This added clarity helps reduce uncertainty and boosts confidence in the results.
Beyond just explaining predictions, XAI can pinpoint potential biases or errors in the data, giving businesses a chance to address them before making decisions. By offering a clear rationale behind each forecast, XAI enables companies to trust and rely on these insights for crucial operations like inventory planning and supply chain management. The result? Improved decision-making and stronger trust in AI-powered tools.
What’s the difference between forecast bias and accuracy in demand forecasting?
When it comes to demand forecasting, two essential metrics to keep an eye on are forecast bias and accuracy. Though they’re closely related, they serve different purposes in evaluating your forecasting performance.
Bias tells you whether your forecasts tend to lean in one direction - either overestimating or underestimating demand. It’s like a compass for your errors, showing their direction. For instance, if your predictions consistently overshoot actual demand, that’s a sign of positive bias. Conversely, forecasts that repeatedly fall short of actual demand indicate negative bias.
Accuracy, on the other hand, measures how close your forecasts are to the actual demand, without worrying about whether the errors go up or down. Accuracy focuses on the size of the errors, and metrics like MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error) or RMSE (Root Mean Square Error) are often used to quantify this.
By examining both bias and accuracy, you can uncover whether your forecasts are systematically off-track or just scattered. This insight is invaluable for improving inventory planning and making smarter decisions overall.
Why is it important to consider both bias and accuracy in demand forecasting?
When it comes to demand forecasting, accuracy and bias are two sides of the same coin. Accuracy tells you how close your predictions are to the actual demand. This is crucial for keeping your inventory in check - avoiding stockouts while reducing the costs tied to overstocking. On the flip side, bias uncovers patterns of consistent error in your forecasts. Are you regularly overestimating demand? Or underestimating it? Either way, these systematic mistakes can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
Striking the right balance between accuracy and bias is the key to building trust in your forecasting system. It ensures decisions are grounded in reliable data, giving you the confidence to plan smarter. This is where Explainable AI steps in. By shedding light on where biases exist and how they impact your forecasts, it helps you refine your models. The result? Better transparency, fewer risks of overstocking or running out of stock, and a supply chain that runs more efficiently - all of which contribute to stronger profitability.


